MSG: The next generation...
NOTE: Some info here is outdated!
On august 29 2002 the first of a new generation weathersatellites was launced: Meteosat Second Generation.
Eventually this generation will replace the old Meteosat satellites, designed 25 years ago.
The data transmitted by MSG satellites differs a lot compared to the current first generation Meteosats:
| First gen. (MET7 and lower) | Second gen. (MET 8 and higher)
|
| Data format | APT (analog), HRI | LRIT, HRIT
|
| Data related to frame | Fixed: 4 or 8 frames/line | No relation: packets
|
| Bits coded | No | Yes; Viterbi
|
| Scrambled | No | Yes
|
| Error correction | No | Yes; Reed Solomon
|
| Compression | No | Yes; JPEG
|
| Encryption | partly | LRIT: partly?
HRIT: ?
|
Because of the fixed data/frame relation, the straight-forward bit transmission and the absence of compression the HRI format is very simple to handle. It is even possible to plot the picture by means of a "picture drum", without the use of a computer.
This simplicity has also its draw-backs:
- Because of the fixed data/frame relation there is not much flexibility in transmitted picture sizes
- Because of the straight-forward bit transmission the sensitivity to noise is 'high'; the only way to increase the quality is by 'brute force': big antennas, powerfull transmitters and low-noise receivers.
- An errored bit is not corrected, not even recognized as such
- Because of the absence of compression the amount of data to transmit is high (i.e., the time to send one picture is long)
MSG transmits its data in a much more complex /sophisticated way, giving the following advantages:
- Viterbi-encoding (K=7, n=2) gives 5 dB better sig/noise ratio, at a cost of 3dB more bandwidth
- By adding extra bits in each block of data error correction is possible
- JPEG compression can lower the amount of bits to transmit up to a factor 10
(or more)
- The packet-like transmission makes it possible to efficiently transmit any size of picture, or other types of data, if needed.
2002...2014
Just like the old Meteosat sends its data in 2 flavours (APT, HRI)
MSG has also 2 flavours: LRIT and HRIT. These 2 digital formats are very similar.
Difference is that HRIT has 10 bits per pixel (LRIT: 8) and HRIT is lossless compressed (LRIT: lossy JPEG).
Also, the modulation is different: BPSK for LRIT, QPSK for HRIT. Which means that the receivers for both formats are different.
Because of a burned-out transmitter in MSG1 all data is now distributed using the Hotbird satellite. Advantage for amateurs is that the equipment needed to receive MSG is very easy to get:
- A small dish, same type as used for satellite TV (80 cm, I use a 60cm offset disc aimed to Eurobird at 9 east)
- Skystar 2 TV tuner, pluggable into a PC (there is also a version to be connected via USB). Note: Other than skystar2 tuners are not guaranteed to work together with the Tellique software!
- A 'fast' PC (1GHz is more than enough) with 'lots' of disk space (with a 80G disk you can play a lot)
- Software to translate the data from the TV tuner into files on disk (Tellique software) and a key to decrypt the data, bot available at Eumetsat for in total 100 euro (amateur use only)
- Software to translate the files into viewable pictures
2015...
From 2018 on direct LRIT reception isn't available anymore. Also,
a bit more expensive and less easy to get equipment is needed.
The tuner MUST be of type DVB-S2 with variable transmission, like SR1 of Ayecka!
Simple/cheap TV-tuners cannot be used anymore.
Postprocessing
For the translation software I did make 'xrit2pic'. It is free available, see further on my website.
Trouble-shooting Eumetcast
Summary.
Signal path:
- Receiver
- Tellicast
- EKU
- ==> File
- Postprocessing: xrit2pic, weview etc.
Receiver.
Data is filtered by means of PID's One pid Must always be present:
- 100 (decimal): the message channel.
The other PID's are optional:
Tellicast: Who is afraid of red, yellow and purple?
Note: following info may not be complete, or even 100% correct.
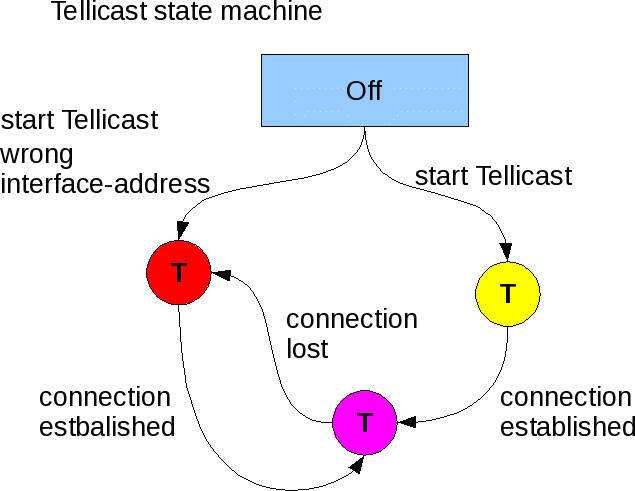
A running tellicast will show a coloured T in your Icon bar.
It can show 3 different colours:
- Yellow: Tellicast is trying to establish a connecion.
It stays yellow if no connection can be made, e.g. because:
- firewall blocks connection
- nothing received
- wrong satellite received
- PID 100 not enabled
- There is no ethernet route between receiver and Tellicast. See below
- Purple: OK, PID 100 Eumetcast data received.
- Red:
- interface_address wrong (recv.ini; 0.0.0.0 is "always OK")
- Connection lost, i.e., there was a connection (purple T) but connection was lost
because of one of the reasons mentioned near Yellow T.
Note that if nothing changes the T stays red, but if you restart Tellicast the T becomes yellow! (Except if interface_address is wrong.)
So the only difference between yellow and red is the past.
Note: Following items do NOT influence your T-colour:
- missing/malfunction EKU
- wrong user address
- wrong password
Note IP connection: This depends on what type of receiver you use.
- Ethernet receiver, like SR1 Ayecka: 2 possibilities:
- Use recv-channels.ini to choose which channels to receive: set interface_address=0.0.0.0 (in recv.ini)
- Choose by routing (e.g. using ecast_cfg on Linux): set interface_address to the destination address
of your choice and route all channels you want to receive to that address. Define in recv-channels.ini to receive 'everything'.
- USB receiver: this will use a dummy ethernet address which you can choose; it must be identical to what is in recv.ini. Common used:
192.168.238.238
EKU
Make sure that the EKU you use belongs to the user_name and user_key in your recv.ini.
If you don't have a key then define:
[recipient]
user_name=eumetcastuser
user_key=9Ecast3004us
You will then only receive the 'free' data.
Checking EKU.
To check that the EKU is correctly installed and working
you can do the following (start one by one the needed programs) (tested on Linux)
| step | Command | expected reaction | fail
|
| 1 | etoken start | etoken 1 flash | etoken not (correctly) installed
|
| 2 | pcscd start | etoken 1 flash | etoken or pcscd not (correctly) installed
|
| 3 | tellicast-client_v2.14 start | etoken several flashes |
|
| 4 | http://127.0.0.1:8100
(8200 for HVS1, 8201 for HVS2) | browser: host_key_4="****..." |
|
Do the above commands one by one. If a command fails (see 'expected reaction') then this needs to be fixed first.
Deactivate start tellicast at boot (Windows).
Navigate using e.g. 'This computer' to:
- local station C:
- Documents and Settings
- (user-name)
- Menu Start
- Programs
- Opstarten
At this place you should see an icon 'pink T', called 'BisinessTV-IP
- Create a new directory, e.g. 'off'
- Move the link to this directory
Now Tellicast wil not start anymore a boot-time.
By moving the link back to the original place you can restore the auto-start-at-boot.

